Chlorhexidine – Multi-purpose Antiseptic

Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic that prevents the growth of bacteria in body tissues. Bacteria are the main causes of infections.
The difference between a disinfectant and an antiseptic is that they work on different surfaces. The former inhibits the growth of bacteria in inert materials, while the latter acts on living tissues such as the skin.
The purpose of chlorhexidine in the oral mucosa is to kill and prevent the growth of bacteria. In this way, it reduces the risk of wound inflammation without being too aggressive to the area to be treated.
This compound attaches to the oral mucosa and is gradually released over approximately eight hours. For this reason, rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine is recommended two to three times a day.
Uses of chlorhexidine
This antiseptic is regularly used in dentistry, especially for the treatment of small wounds in the oral mucosa. Chlorhexidine treatments can be either general or local, depending on the area being treated.
General care
You have probably used chlorhexidine if you have a chronic tendency to have oral aphthous or other similar oral problems. Experts recommend using chlorhexidine as a mouthwash after brushing your teeth. This ingredient is also present in some toothpastes.
Local damage
Chlorhexidine can be used as a spray to treat local lesions, as the effect of this dosage form is more local and precise. Topical use of this antiseptic is intended for the following situations:
- Inflammation of the mouth
- Tongue ulcers
- Postoperative care

Use of chlorhexidine in special oral treatment
In the treatment of the mouth, chlorhexidine is usually used diluted to concentrations of 0.2%, 0.12% and 0.10%. It can be used in various forms such as gels, sprays and toothpaste. Chlorhexidine mouthwash should be used for half an hour after brushing your teeth by sprinkling it for a little over half a minute.
In the treatment of local lesions, such as after dental surgery, experts usually recommend a spray because it has two significant benefits:
- The effect is more local
- The antiseptic effect is higher
This antiseptic should not be used for a long time as it can stain teeth as well as darken the gums. However, do not worry if this happens, as the effect will disappear after you stop using it.
Recommended use
Most people use chlorhexidine immediately after brushing their teeth as if it were a frequently used mouthwash. However, this is not an orthodox way of using it. In fact, the best time to use it is at least half an hour after brushing your teeth.
This is recommended because chlorhexidine is incompatible with certain ingredients that many toothpastes contain. These ingredients include sodium lauryl sulfate and sodium monofluorophosphate.
Use of chlorhexidine as a topical antiseptic on the skin
Chlorhexidine can also be used as a topical antiseptic on the skin because it is effective against a wide variety of different microorganisms. It has many benefits, including not rubbing or irritating. It also does not react with blood. In addition, this compound is almost non-toxic and can be used for open wounds such as abrasions, cuts and burns.
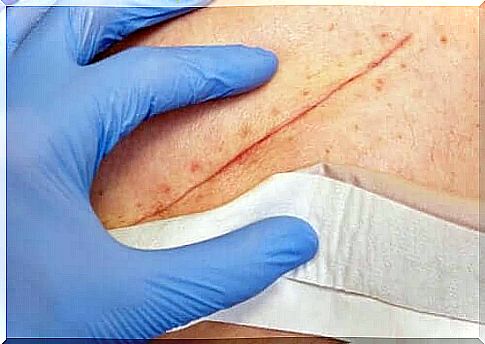
What side effects can chlorhexidine cause?
There are no significant side effects associated with the use of this compound, but some allergic reactions and rashes may occur in the treated area in a small proportion of users.
As mentioned above, long-term use of chlorhexidine in oral care can stain teeth and intensify coffee- and tobacco-induced discoloration.
Chlorhexidine is an essential antiseptic
Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic that is particularly effective against bacteria and fungi. It is used a lot around the world, so much so that it has reached the World Health Organization’s list of essential medicines.