Corneal Tumors: Tension And Pterygium
The eyes form one of our senses: the visual organ. Therefore, we should pay attention to any anomalies affecting the eyes. In this sense, corneal tumors, such as the pinguecula, or pterygium, are quite common ocular abnormalities, which we delve into in more detail in this article.
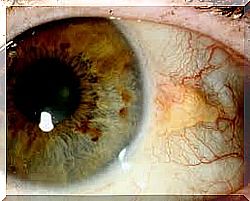
Both of the above tumors are the result of conjunctival degeneration. Tension gullet occurs as a small lens or button in the white area of the eye (sclera) and can sometimes be inconspicuous. On the other hand, pterygium is the result of abnormal growth of the conjunctiva due to an inflammatory process.
Although the size of the tongue ball is usually insignificant, it can increase over time. In most cases, its size does not directly affect vision. In fact, some people may have more than one conjunctival nodule in their eye completely unknowingly.
Read more below about the most common causes of penguinula, its symptoms and treatment, and how it differs from pterygium.
What are the most common causes of tension?
According to experts from the American Academy of Ophthalmology in California, the causes of tension can be as follows:
- Exposure to dust and wind
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet light
- Body fat percentage
- Dry eyes
- Hormonal changes
- Certain medicines
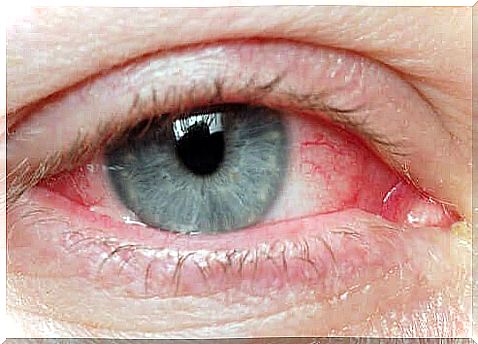
Symptoms of tension
- Itching of the eye or redness of the eyeball, especially near the cornea, pupil and iris
- Dry eyes
- Irritation in the affected area
- Constant swelling
- Feeling of rubbish in the eye
How is tension gland treated?
This condition usually does not require treatment. An ophthalmologist may recommend the use of moisturizing eye drops if the tension gullet causes eye irritation.
In more severe cases, where this damage directly affects vision or causes symptoms that do not disappear with moisturizing eye drops, surgical treatment may be used.
In these cases, very severe inflammation is observed in the conjunctiva of the eye, leading to persistent redness and itching.
It should be noted that in these cases, the surgery does not require hospitalization and the operation is treated with local anesthesia and does not take much time. However, there are certain risks associated with every surgical intervention, so surgery should always be the last resort.
After surgery, the patient should wear an eye patch for maximum protection for two days, unless otherwise recommended by an ophthalmologist.
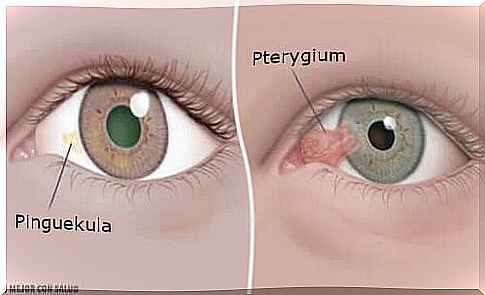
How does the penguin differ from the pterygium?
Although both, the pinguecula and the pterygium, are the result of abnormal conjunctival functions, we are talking about two different conditions.
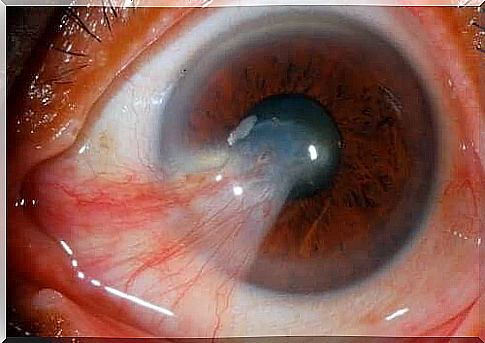
Pterygium is composed of an abnormality of the eye and is manifested by a thickening formed in the eye that resembles the color of the skin as opposed to the penguin, which in turn resembles a more yellowish color.
Pinguekula and pterygium are also not located in the same place in the eye. Pterygium usually develops from one end of the conjunctiva toward the cornea, whereas tension is usually found directly in the sclera of the eye and rarely affects the cornea.
In the case of pterygium, a tumor that has reached a significant size can change the surface of the eye and lead to vision problems.
Similarities between pinguecula and pterygium
The first similarity between the pinguecula and the prerygium, as we mentioned earlier, is that both conditions result from an abnormality of the conjunctiva of the eye, a thin layer of connective tissue that covers the eyeball.
Both diseases initially cause similar symptoms, so confusion between the two tumors is not uncommon.
In these circumstances, experts recommend preventive measures, especially by avoiding the most obvious cause, i.e. exposure to ultraviolet radiation. To achieve this, we should ensure that sunglasses have adequate UV protection against ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Another important factor that can trigger tension and pterygium is age. In fact, both tumors occur much more often at the age of more than 40 years. Therefore, routine eye examinations allow for the early detection of both the above and many other more serious eye problems.