Myocarditis: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment

Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle. The heart muscle is called myocardium and its function is to move the heart. It contracts to send blood around the body and then relaxes until the heart begins to fill again.
If the heart muscle becomes inflamed, the heart’s pumping function is no longer as effective and its cells are damaged. Naturally, this is a significant health risk.
It is not certain exactly how many people suffer from myocarditis, as myocarditis in many cases does not cause any symptoms. However, it can occur at any age, including children.
What causes myocarditis?

In at least half of the cases, myocarditis is caused by an infection caused by viruses, fungi, parasites or bacteria. It often occurs as a result of diarrhea, flu, or flu.
Other common causes of myocarditis include:
- Allergic reactions to drugs
- Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as heavy metals
- Radiation
- Autoimmune processes that cause inflammation
In addition, the development of myocarditis is associated with some diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatic fever and rubella. Sometimes the exact cause of the disease is impossible to determine.
What is myocarditis
The body responds to inflammation of the heart muscle by activating the immune system. The immune system sends antibodies to fight the inflammatory factor. But the chemicals produced by these cells can damage the heart muscle.
If a lot of cells are damaged, the result is a weakened and inflamed heart. When this process happens very quickly, it can lead to heart failure and sudden death.
Normally, however, the heart regenerates on its own. It does this by replacing damaged or dead heart muscle cells with scar tissue. The scar tissue is stiff and therefore does not promote heart pumping.
When scar tissue is very widespread, it can cause heart failure or dilating cardiomyopathy.
Symptoms of the disease
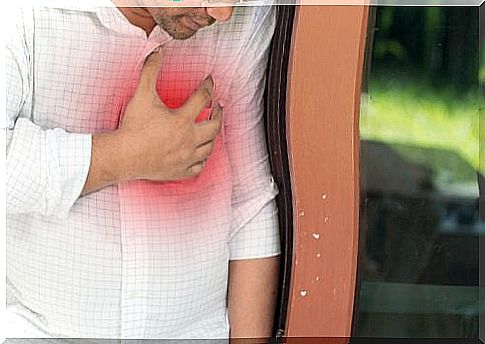
The symptoms of myocarditis are very variable. In fact, in some cases, the symptoms do not appear at all.
In any case, it is important to remember that there is both acute myocarditis and chronic myocarditis. Each has its own symptoms.
The symptoms of acute myocarditis are similar to those of heart failure. The most important of these are:
- Intense and sharp chest pain behind the sternum
- Tachycardia
- Bluishness or pallor of the skin and mucous membranes
- Shortness of breath
- Arrhythmias
- Inflammation of the liver and spleen
- Accumulation of fluid in the feet
The symptoms of chronic myocarditis are less clear. In general, it causes a feeling of weakness, exhaustion and shortness of breath with even a small amount of effort, changes in appetite, pain in the limbs and weight loss.
Diagnosis and treatment
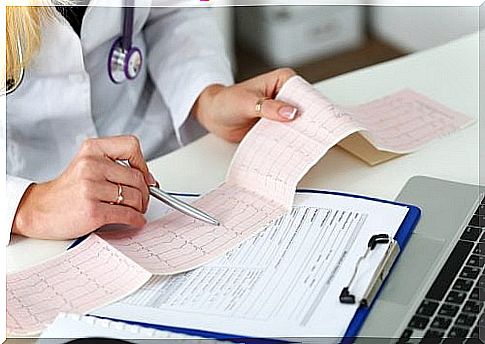
Diagnosing myocarditis is problematic because the symptoms are not very clearly associated with myocarditis, and thus can be misinterpreted as caused by another disease.
Usually, the doctor will first perform a clinical examination to confirm the existence of symptoms and to obtain information about the patient’s recent infections.
If in doubt, your doctor may refer you to x-rays to determine if there is fluid in your lungs. However, the most common examination is the ECG, or cardiac film. It allows the doctor to get accurate information about the functioning of the heart.
The most accurate method is to take a piece of myocardial specimen. The results give a definitive diagnosis, as the test directly shows whether the heart muscle is inflamed or not. This test is usually prescribed when myocarditis is suspected.
In most cases, acute myocarditis goes away on its own. It heals itself, leaving no repercussions. Sometimes the disease is more severe and can lead to more serious problems or death. In some cases, it may lead to permanent heart failure. It all depends on the general health of the patient and the factors that caused the disease.