Postpartum Hemorrhage: Prevention And Treatment
Postpartum bleeding is a significant risk for a woman. It is one of the biggest postpartum complications around the world. What causes it and how is it treated?
Bleeding after childbirth
Postpartum hemorrhage is defined as blood loss of more than 500 ml after subcutaneous delivery or 1 liter of blood loss after caesarean section. Worldwide, 75% of post-pregnancy complications are due to bleeding.
Postpartum hemorrhage is the leading cause of death for women who have given birth in underdeveloped countries. In fact, they cause nearly a third of all women who give birth.
One third of the cases do not involve risk factors or known causes. Bleeding can occur in all women after all kinds of births. However, the four most common reasons are:
- Uterine atony: inability of the uterine muscles to contract.
- Vaginal or cervical injuries.
- Placental remnants in the uterus as a result of labor problems.
- Blood clotting disorder.
Postpartum bleeding: prevention and treatment
When bleeding occurs, it is important to receive prompt and effective treatment to prevent maternal mortality. Today, methods to prevent postpartum hemorrhage have reduced mortality rates in developed countries.
The goal is to reduce the number of risk factors for the mother giving birth.
Childbirth monitoring
Childbirth also involves straining the placenta out after the baby is born. The more the uterus contracts, the shorter and more effective this stage of labor is. This reduces the risk of bleeding.
Postpartum bleeding can be prevented at various stages. First, the mother giving birth may be given medications to increase uterine contractions that shorten the duration of childbirth.
The most common such drug is oxytocin. If oxytocin is not available, doctors may use misoprostol, for example. The doctor should also palpate the woman’s abdomen from time to time to ensure that the uterus is shrinking sufficiently.
One procedure performed by physicians may be early ligation of the umbilical cord associated with manual removal of the placenta. However, this is a controversial method.
Prevention of perineal tears
The diaphragm is located between the genital area and the anus. In uncontrolled labor, ruptures of the perineum are common and can cause bleeding after childbirth. For this reason, some women undergo an episiotomy, or surgery on the perineum. In this method, a small controlled incision is made in the perineal area.
Episiotomies are also an effective way to prevent uncontrolled bleeding and prevent future problems. They can be used to avoid pain or bad scars, for example.
Treatment of anemia during pregnancy
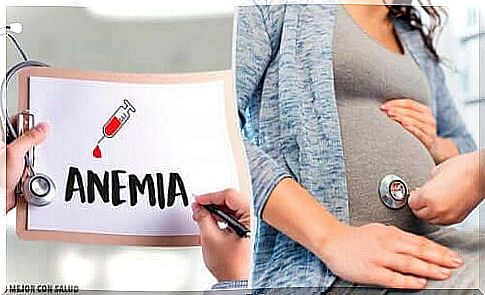
Anemia can exacerbate post-pregnancy bleeding, which is why diagnosing and treating anemia is also some way to prevent excessive bleeding.
However, the success of anemia prevention may depend more on early initiation of supplements than on their amounts. It is therefore recommended that all pregnant women eat iron and folic acid supplements no later than the ninth week of pregnancy.
Minimization of perineal tears in assisted delivery
Sometimes doctors may need to use special tools to help with childbirth. Whenever possible, you should choose the equipment that causes as little damage as possible.
Assisted deliveries should primarily use the suction cup.
Transfusion
Postpartum bleeding can cause severe blood loss, which is why a blood transfusion may sometimes be needed.
Finally
Postpartum hemorrhage is one of the most common fatal postpartum complications in the world. Because they are a risk to all mothers, it is important to monitor your pregnancy from start to finish.
In addition, if bleeding occurs, help should be obtained as soon as possible to ensure the best possible prognosis.