What Is A Groin Hernia?
Do you know what a groin hernia is?
Generally, a hernia is a protrusion that is usually located in either the abdomen or groin. It occurs when there is a weak spot in the body or when there is a hole in the abdominal wall.
Typically, a hernia is caused by a problem in the structure of body tissues and manifests as a bulge.
The groin hernia can be an inherited or lifestyle phenomenon. For example, if a young child gets this type of hernia, it is usually a hereditary ailment, and in an adult, the cause is usually lifestyle.
- Hereditary hernia in newborns requires immediate surgery. In these cases, they usually occur in conjunction with a problem seen in the womb.
- When a hernia develops again, 50% of cases are caused by inflammation.
Lifestyle hernias occur in adults. Most often, they are due to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure due to , among other things:
- pregnancy
- work that involves heavy lifting or tensioning the abdominal muscles
- diseases such as COPD
- prostate and the difficulty associated with urinating

In addition, the hernia may be encapsulated.
- A non-encapsulated hernia looks like a mass that either appears or increases when you are straight. So coughing or standing makes it bigger, while lying down makes it decrease.
- Once the hernia is encapsulated, it does not grow or shrink at all.
Why does a hernia develop so easily in the groin or stomach?
All hernias develop in areas with “anatomical weakness”. This means the areas where the anatomical walls are weakest. This is easy for the anterior abdominal wall as it is much weaker than the posterior wall.
Groin progression
- This is one of the most common diseases. It is estimated that one in 30 people will suffer from it at some point in their lives.
- Surgery to treat a hernia covers 15% of all general surgical procedures. Thus, this is one of the most common types of surgery.
- Groin and femoral hernias are the two most common types of hernias. Groin hernias are more common in men, while thigh hernias are more common in women. Hernias are the second most common cause of intestinal obstruction due to a mechanical factor.
- The frequency is also quite high. In half of the cases, it is related to inflammation.
Classification of the groin hernia
The groin is classified based on the ratio of the intestine to the point where the hernia travels through the groin channel. The categories are as follows:
Straight groin
The intestinal loop intersects with the base of the groin canal.
The hernia can descend into the upper abdominal artery and will not pass through the deep opening of the groin plan. It is located behind the Cremaster muscle but is not connected to its fibers.
This type of hernia often occurs in the elderly.
Indirect groin hernia
This is the most common type of hernia in both men and women. In this case, the hernia protrudes into the groin channel towards the scrotum in a man, and towards the outer labia in a woman.
In this situation, the intestinal loop is lateral to the abdominal artery. In some men, the bowel loop may be inside the testicle.
Symptoms
In general, groin hairs produce only mild symptoms.
In most cases, the patient feels good in the morning. As the day progresses, however, you begin to notice discomfort when you exercise, cough, or do something similar. In many patients, pushing the hernia back is possible at home.
Narrowing means that blood is not possible at the hernia formed by the bowel in the bend. This is an emergency that requires surgery and the gut has little resistance to periods of ischemia. In this case, there is also a risk of death.
When a hernia complication occurs, it can no longer be pushed back in. In addition, the pain is usually very severe, in addition to which a fever may occur.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made using a simple experiment, while at the same time examining the patient’s medical history. In fact, the patient does come to the hospital knowing he has a hernia. Still, it is important for all patients with abdominal pain to be examined.
Care
Treatment goals
Surgical hernia repair is based on the following:
- Restoration of the intestinal loop into the abdominal cavity without opening the peritoneum, if possible.
- Identification of membrane tendon edges.
- The hole in the closure, which caused the development of the hernia.
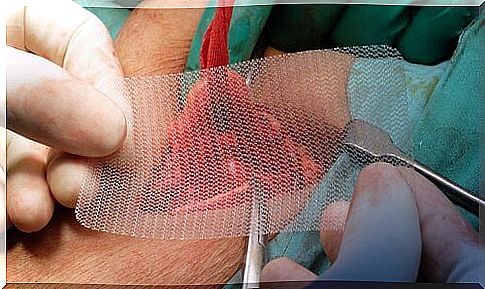
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment of the groin hernia can be performed using either open surgery or laparoscopy.
Minimally damaging groin surgery is both a good and a bad option compared to traditional techniques.
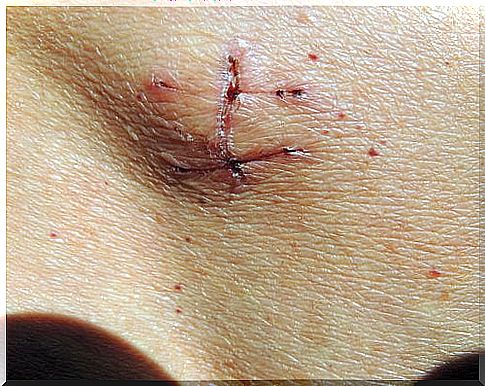
On the other hand, it reduces postoperative pain and recovery time, and leaves an aesthetically better outcome.
On the other hand, it has a higher chance of complications both during and after surgery. It can also increase the risk of recurrence, cost more, and produce surprising long-term side effects.
For these reasons, this is still a controversial measure that has both supporters and opponents.
Frequency
This is defined as the reappearance of a hernia in the same area. Depending on how the hernia manifests, it can develop immediately or later.
Recurrence depends on many factors, some due to the patient and others due to surgery.
Patient-related factors include:
- age
- hernia type
- other diseases
Factors related to surgery include:
- inexperience
- poor technology
- inaccurate diagnosis