What Is The Difference Between Prebiotics And Probiotics?

While both are beneficial to our health, in essence, prebiotics and probiotics differ in their function and in what products we can find them. In this article, we want to find out more about the difference between prebiotics and probiotics.
There are millions and millions of microbes in our bodies that live together with our cells: all of these microbes, in turn, build one large entity that we call the human microbiota. Many of these microbes live in the gut and for this reason the normal bacterial strain in the gut is called the bacterial flora, or microbiome.
All of these intestinal bacteria can be divided into two different types: bacteria that have beneficial effects and bacteria that have harmful effects. The latter bacteria can cause, for example, diarrhea, infections or the breakdown of good bacteria in the gut.
Beneficial bacteria, in turn, will help us to control the harmful bacteria, stimulate the immune system, reduce gas generation and improve digestive function. They are also necessary helpers for the synthesis of some vitamins as well as for the absorption of certain nutrients.
Therefore, in order to maintain a good mood and health, it is very important that we keep the intestinal bacterial flora healthy and in balance. But what do prebiotics and probiotics have to do with all this? We will delve deeper into the subject next.
The main difference between prebiotics and probiotics
To maintain the health of the intestinal bacterial flora, we need to take care of two basic tasks:
- Provide our bodies with probiotics to ensure that our body is constantly living with beneficial microbes.
- Provide our bodies with prebiotics to nourish the microbes that live in our bodies.
In summary, we can see where the main difference between prebiotics and probiotics lies; or at least one of the main differences so that we can distinguish between these two important microbial strains.
Now, however, we want to dig a little deeper into the workings of both and find out what kind of products we can find them in. So keep reading!
Prebiotics are the food of the bacterial flora of our intestines

Prebiotics are indigestible ingredients in the digestion that reach the gut intact. When they enter the gut, they act as food for intestinal bacteria, which in turn find the right enzymes to break down prebiotics.
By providing food for these bacteria, prebiotics stimulate their growth and activity, and ultimately also improve the health and well-being of the host (our people). In order to be considered a prebiotic, a food ingredient must meet the following three conditions:
- It does not break down or be absorbed in the stomach and small intestine.
- Bacteria can ferment it when it enters the colon intact.
- This fermentation must promote the activity and multiplication of bacteria in the gut which have a beneficial effect on the human body.
To date, the most studied prebiotics have been the different types of fiber found in plant-based foods. These include, in particular, oligofructoses, i.e. fructooligosaccharides (FOS), galactans, or galactooligosaccharides (GOS), and inulin.
However, we can also find many beneficial substances for the intestinal bacterial flora in other foods:
- Foods containing some types of fiber; for example, onions, leeks, asparagus, artichokes, seeds (such as chia and flax), potatoes, carrots, and apples are good sources of prebiotics.
- Prebiotics can also be found in the polyphenols of cocoa, red fruit, and some spices.
- Olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish are also known to contain prebiotics useful for the bacterial flora of the gut.
So what are probiotics?
Now that we know what prebiotics are, we can delve deeper into the concept of probiotics to get a clearer picture of what the difference between prebiotics and probiotics really is. The term probiotic literally means “for life or for life”.
The most accepted definition of a probiotic has been formulated by the World Health Organization and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). These organizations have defined probiotics as follows:
In this context, we are no longer talking about feeding the bacteria, but about helping the bacteria themselves. Most probiotics are derived from the bacteria used to ferment food.
The most studied probiotics belong to the genus Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. In addition, we can find them in the form of both foods and food supplements.
The main sources of probiotics

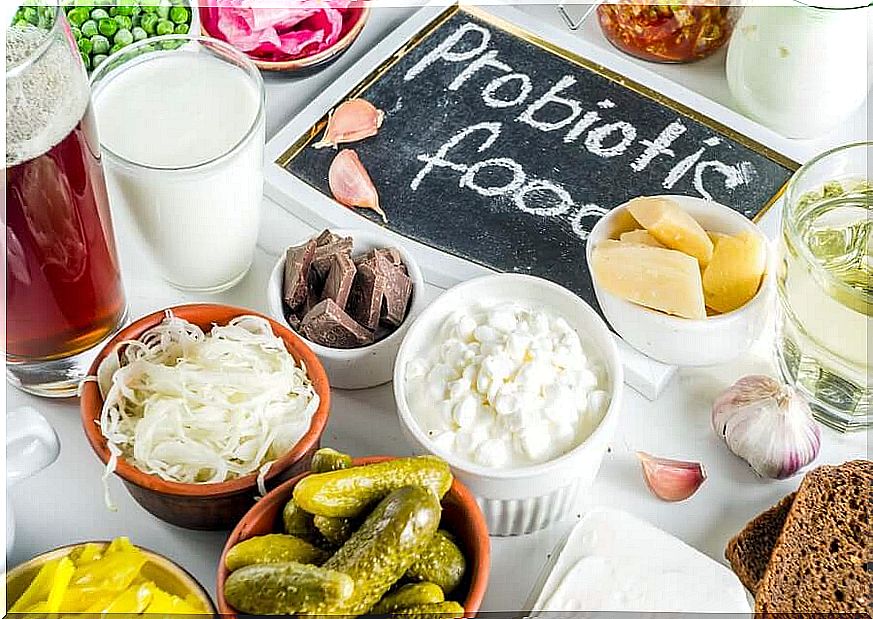
We can say that one of the most affordable foods with the most probiotics and used on a daily basis is definitely traditional yogurt. And there is no need to add anything to it. Natural yogurt provides us with lactobacillus and streptococcal probiotics that are important for the intestinal bacterial flora. Kefir is also another ideal choice for obtaining probiotics , as it offers us even more diverse bacterial strains than natural yogurt.
One great source of probiotics is fermented vegetables such as sauerkraut and pickles. In Asian cuisine we can find miso paste and tempe made from fermented soybeans.
Finally, we need to mention one interesting option that provides us with a significant source of probiotics; kombucha, a lightly carbonated beverage that has become a very popular food in recent years.
Finally
Perhaps the most comprehensive summary we can draw between prebiotics and probiotics is to understand that they have a different but at the same time complementary effect. For the same reason, it is of no use if we provide our bodies with probiotics if they do not end up getting adequate nutrition from prebiotics.
However, we must also remember to keep an eye on the latest winds in the subject area, as the science surrounding prebiotics and probiotics is expanding and evolving day by day so that it can bring us many new concepts and observations in the near future.